While disciplinary knowledge is important for developing expertise in a specific area, interdisciplinary knowledge is crucial for solving real-world problems that require a holistic approach. Interdisciplinary research and learning can also foster creativity, innovation, and new perspectives on complex issues. However, interdisciplinary work can also be challenging, as it requires individuals to navigate different academic cultures, languages, and methods.
In conclusion the difference between the two is that disciplinary knowledge is deep and narrow, while interdisciplinary knowledge is broad and diverse, and combines knowledge from different disciplines to address complex problems. Both approaches have their strengths and limitations, and they are often used in complementary ways to advance knowledge and understanding in various fields.
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is a flexible and customizable framework that can be adapted to the specific needs of different organizations. It is widely used in various industries and sectors, and it has become a de facto standard for managing cybersecurity risks. By following the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, organizations can improve their cybersecurity posture, reduce their risks, and enhance their resilience against cyber threats.
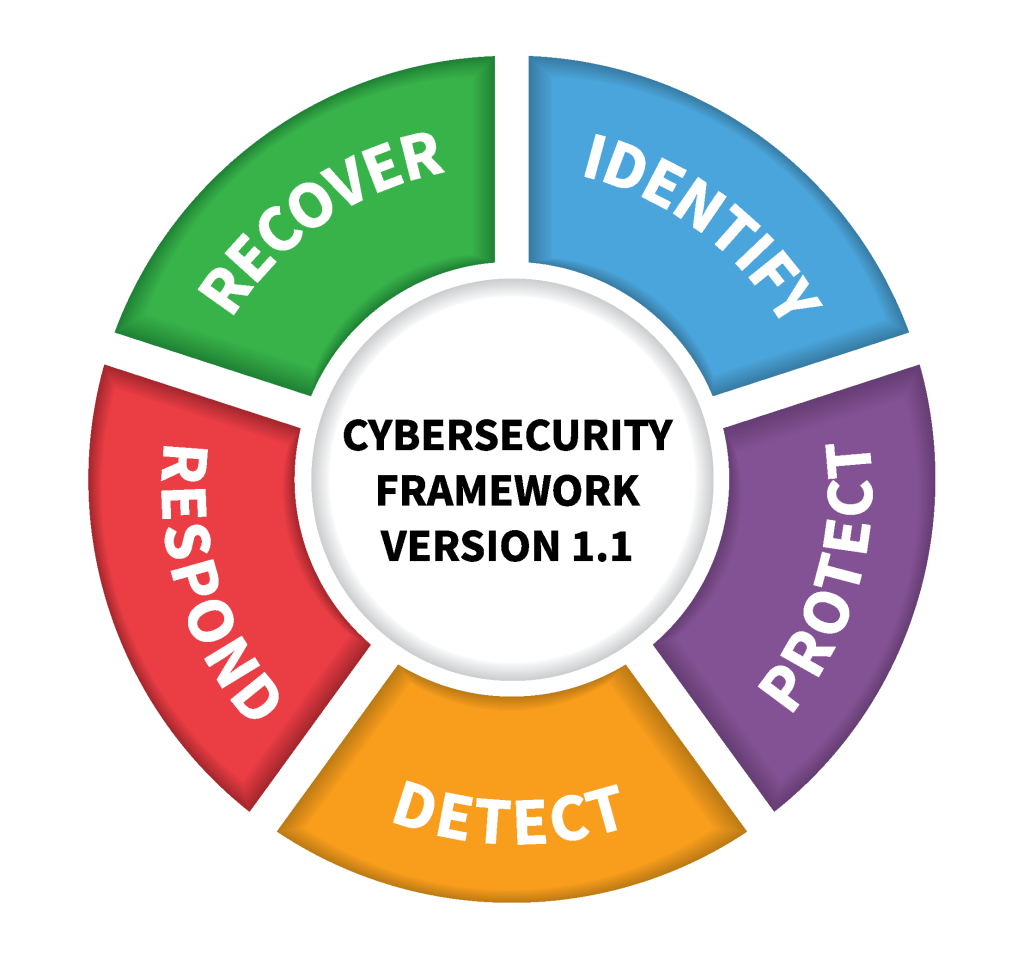
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) developed a widely used cybersecurity framework that includes five core activities:
Identify: This activity involves developing an understanding of the organization’s cybersecurity risks, including its assets, threats, vulnerabilities, and impacts.
Protect: This activity involves developing and implementing safeguards to protect the organization’s assets from cybersecurity threats. This may include access controls, encryption, firewalls, and other security measures.
Detect: This activity involves developing and implementing methods for detecting cybersecurity events, such as intrusions or data breaches, in a timely manner. This may include intrusion detection systems, log analysis, or other monitoring tools.
Respond: This activity involves developing and implementing a response plan for cybersecurity incidents. This plan should include procedures for containing the incident, assessing the impact, notifying stakeholders, and recovering from the incident.
Recover: This activity involves developing and implementing strategies for restoring the organization’s systems and data after a cybersecurity incident. This may include backup and recovery procedures, testing, and contingency planning.

Leave a Reply