CYSE 201S
Week 1 – The NICE Workforce Framework
The NICE workforce framework has seven distinct categories analyze, collect and operate, investigate, operate and maintain, oversee and govern, protect and defend, and securely provision. There categories are a high-level grouping of common cybersecurity functions as well as help define the distinct area of cybersecurity work. This allows one to view these detailed groupings of the type of knowledge and specialization each require for careers that focus on said categories. After reviewing the NICE workforce framework there are a few areas I personally would prefer to focus on. That being collect and operate, investigate, and protect and defend. Said categories appeal to me due to the tasks and knowledge associated with the respective set of categories. The one that for me personally has the least appeal would be operate and maintain. The reason it holds the least appeal is in the specialization towards administrative tasks which to me personally would feel monotonous.
Week 2 – How the Principles of Science Relate to Cybersecurity
The scientific principles of determinism, relativism, objectivity, parsimony, skepticism, and ethical neutrality can be applied to both the study and application of cybersecurity.
- Determinism: In relation to cybersecurity determinism might refer to the idea that actions done by threats such as hacking or exploiting a vulnerability in a system is determined by a cause-and-effect relationship were every cyber event could be traced back to specific factors such as stated before vulnerabilities, weak security measures, or malicious threats. A way to apply this principle to the study of cybersecurity would involve analyzing the cause-and-effects of cyber threats.
- Relativism: When applying the principle of relativism to cybersecurity would be to acknowledge that the perception of security itself can vary depending on the context of the situation. Different organizations might have different security needs in which they prioritize defending against different risks. In application of studies one could factor in these differing needs and perspectives to help devise strategies and evaluate risk assessments.
- Objectivity: Can very easily be applied to cybersecurity as it would be basing decisions on factual information and unbiased analysis rather then anecdotal or subjective opinions. This would mean practicing a rigorous examination to prove its integrity and moreover a critical evaluation of how organizations that suffered from cyber threats.
- Skepticism: This principle is also one that easily relates to cybersecurity as it can be seen as an almost essential mindset to question assumptions, claims, and best practices already put in place by an organization. As one needs to ensure that the already in-place measures are valid and effective.
- Parsimony: This principle also colloquially called Occam’s Razor would suggest that the simplest explanation that can adequately explain a situation is often the correct one. In relation to cybersecurity this would mean trying to make the simplest effective security policies to combat security challenges. It would be avoiding unnecessary complexity as it might introduce protentional vulnerabilities into the system or hinder the effectiveness of the cybersecurity measures as a whole.
- Ethical Neutrality: Ethical neutrality in relation to cybersecurity calls for maintaining a neutral stance when it comes to ethics and morality in security practices. It would mean keeping to established legal and ethical industry standards while ensuring the protection of sensitive data, user privacy, data integrity, and the integrity of systems as a whole. An example of an ethical consideration might be disclosing discovered vulnerabilities or reporting when an organization has suffered a breach from a cyber threat.
Week 3 – How Researchers can use publicly available information about data breaches
Researchers can use the publicly available information on websites such as PrivacyRights.org to study data breaches. Researchers can utilize this publicly available information in various ways such as for risk assessment, as the breach data can be utilized to assess the method used to breach the network, the type of data that was compromised, and the vulnerability that was exploited to help identify critical risks that could help inform other organizations potentially vulnerable to a similar attack. In the same vain this information could also be used to help shape detection and prevention strategies being able to quantitively review either the most common attack vectors or the most successful attack vectors.
Week 4 – Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and How it Relates to my Experience with Digital Technology
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a psychological theory that suggests that human needs can be divided into five distinct levels which are arranged into hierarchical order. The first level being the bottom of the hierarchy which is physiological needs which is the followed by safety needs, belongingness and love needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs. Each of these build upon the previous one and can be applied to how we use and experience technology.
- Physiological Needs: Technology has made this need easy to fulfill and in the digital space things such as ordering food online or on your phone have become ever more commonplace. Other instances that digital technology has helped me fulfill my physiological needs is paying online for my rent to secure shelter, and paying my water bill online to have on-demand clean drinking water.
- Safety Needs: Safety needs when applied to my experiences with digital technology could be the online payment security measures which encrypt my data during transmission, or any security measure that is in place for data integrity.
- Belongingness and Love Needs: Digital technology has definitely helped me over the years to fulfill this need as it helps me keep in contact with friends using programs such as Discord. Even as all of us move around we can still be interconnected to a degree and still interact with each other.
- Esteem Needs: Due to my experiences this one is likely underfilled in the digital space as I rarely post publicly in-terms of wanting prestige or the feeling of recognition. Ironically posting on this portfolio could be viewed as a way to fulfill this need. My most use-case for digital technology for recognition might be websites like LinkedIn posting about where I’ve worked and what I’ve worked on.
- Self-Actualization: It wasn’t until the COVID-19 quarantine that I realized how much I utilize digital technology for self-actualization. The main outlet being the creative outlet as during the pandemic was that I hosted TTRPG (Table-Top Role Playing Games) for my friends and it greatly helped both in terms of mental health and having an outlet for my need to create things.
Week 5 – Ranking the Motivations to Commit Cybercrime
- Multiple Reasons: It is hard to pin down a universal motivation for cybercrime therefore it is likely to be multifaceted with a multitude of underlying factors contributing towards pushing people into committing cybercrimes.
- Money: If I had to choose one of the leading motivations that make up the multiple reasons one would be motivated towards cybercrime it would definitely be for financial gain. Simply by looking at the shear quantity of fraud and scams that occurs on the internet from Sam Bankman-Fried’s FTX to pop-up scams targeting the elderly and tech illiterate there is money to be made committing cybercrimes online. Cybercriminal spending habits also to an extent show that as they achieve wealth through their crimes that are able to spend it on luxury products; luxury brands offering their products for crypto-currency seems to show how indicative this is.
- Political: Hacktivism is a strong motivation to commit cybercrime from breaching both government and private organizations. As many of the leaks over the past decade have shown ideologically motivated cyber attacks by hacktivists have occurred and have been successful. Extremists are more likely to act on this motivation; due to it being ideologically motivated, and actually fully commit to stealing data in a breach.
- Revenge: If someone wanted to be malicious online for revenge most people don’t really have the security measures in place to protect themselves. Actions such as doxing people, or posting sensitive private photos of someone online do occur. Likewise someone if given enough information can impersonate you online to slander you, or just straight up go for identity theft.
- Entertainment/Boredom: Robert Burnham’s “Apathy is a tragedy and boredom is a crime” in reference to the internet comes to mind when talking about motivation for cybercrime. As social media and the internet have given people constant stimulation nobody can really sit there and be bored. So more vulnerable demographics can be the target of alleviating the boredom, or if they have the skillset going down the rabbit hole of seeing how far they can get into an individuals or organizations systems.
- Recognition: Of all the motivations this seems to make the least amount of sense just due to peoples want to stay behind the veil of anonymity online. As gaining recognition for crimes you commit online seems counter-intuitive but people will always have a degree of vanity or not think things through. To me this being the sole motivation for someone to commit cybercrime is very weak and would more likely be a contributing factor in another motivation.
Week 5 – Ranking the Motivations to Commit Cybercrime
- Multiple Reasons: It is hard to pin down a universal motivation for cybercrime therefore it is likely to be multifaceted with a multitude of underlying factors contributing towards pushing people into committing cybercrimes.
- Money: If I had to choose one of the leading motivations that make up the multiple reasons one would be motivated towards cybercrime it would definitely be for financial gain. Simply by looking at the shear quantity of fraud and scams that occurs on the internet from Sam Bankman-Fried’s FTX to pop-up scams targeting the elderly and tech illiterate there is money to be made committing cybercrimes online. Cybercriminal spending habits also to an extent show that as they achieve wealth through their crimes that are able to spend it on luxury products; luxury brands offering their products for crypto-currency seems to show how indicative this is.
- Political: Hacktivism is a strong motivation to commit cybercrime from breaching both government and private organizations. As many of the leaks over the past decade have shown ideologically motivated cyber attacks by hacktivists have occurred and have been successful. Extremists are more likely to act on this motivation; due to it being ideologically motivated, and actually fully commit to stealing data in a breach.
- Revenge: If someone wanted to be malicious online for revenge most people don’t really have the security measures in place to protect themselves. Actions such as doxing people, or posting sensitive private photos of someone online do occur. Likewise someone if given enough information can impersonate you online to slander you, or just straight up go for identity theft.
- Entertainment/Boredom: Robert Burnham’s “Apathy is a tragedy and boredom is a crime” in reference to the internet comes to mind when talking about motivation for cybercrime. As social media and the internet have given people constant stimulation nobody can really sit there and be bored. So more vulnerable demographics can be the target of alleviating the boredom, or if they have the skillset going down the rabbit hole of seeing how far they can get into an individuals or organizations systems.
- Recognition: Of all the motivations this seems to make the least amount of sense just due to peoples want to stay behind the veil of anonymity online. As gaining recognition for crimes you commit online seems counter-intuitive but people will always have a degree of vanity or not think things through. To me this being the sole motivation for someone to commit cybercrime is very weak and would more likely be a contributing factor in another motivation.
Article Review #1: Exploring Fraudsters Strategies to
Defraud Users on Online Employment Databases
Article Research Question
This article explores the social engineering tactics used by fraudsters to defraud users on
advertisement databases. It supposes that in social engineering attacks the “linguistic cues and
tactics, differ depending on a user’s online resume presentation on employment database
websites.” (Cole, 2022).
Relation to the Principles Social Sciences
The study utilizes literature review to help in the exploration of its hypothesis. The study
maintains objectivity in its research and analysis with the aim of studying the tactics and social
cues of online fraudsters. It relies on the contextual evidence of the victim targeted by the
fraudster such as gender, socioeconomic status, education level, and the employment position.
It as well relies on the context of whom the offender is attempting to imitate. This means the
study is exploratory research.
Research Methods Used and Data Analysis
The researcher created eight fake resumes on Indeed and Monster. “The researcher
divided the eight resume profiles by sex, education level, employment position, socioeconomic status, and location.” (Cole, 2022). The researcher collected data by contacting employment
opportunities on Indeed and Monster, in which they applied twice a week. Each fake profile
was linked to a unique e-mail, and cellphone number. All employment opportunities offered to
these profiles was documented. It then used this qualitative data to analyze the messages sent
by offenders using data points such as the count of a specific word and cues. This is used to
differentiate offenders and give them an identity for the study. It then separates the data
further into the type of attack used by the offender.
Relation to CYSE201s
This study at its core is trying to understand victim behaviors that make people more
likely to be the target of fraudsters; in which it is not blaming the victim more so profiling if
gender, socioeconomic status, education level, or ones position they apply to matters to online
fraudsters. This also means that the study is trying to find how the psychology of the offender
applies in these social engineering attacks. In which profiles are built on the verbal and non-
verbal communications from the offenders.
Impact of the Study on Society
The data from the study suggests people applying for low-income positions like
babysitter are more likely to be targeted by offenders. It also infers the offenders are more
likely to target people who only have their GED. This concerns people marginalized by their
socioeconomic status as it implies, they are more likely to be targeted by offenders. That being said the sample size of the study limits the analysis of the data and doesn’t factor in the
technological ability of both the offender and the victim.
Conclusion
This study ended up being a preliminary analysis due to its small sample size. The study
focused on the social engineer used by offenders. As well as the language, verbal cues, and how
they were used to imitate employers. It could not factor in the technological ability of the
offender or the victim. It nonetheless may show the importance of target selection by
offenders. It still is inconclusive due to the findings potentially being chance findings.
References
Cole, T. (2022). Exploring Fraudsters Strategies to Defraud Users on Online Employment Databases.
International Journal of Cyber Criminology Vol 16 Issue 2, 61-86.
https://cybercrimejournal.com/menuscript/index.php/cybercrimejournal/article/view/90/28
Week 6 – What Makes a Fake Website Fake
One of the most common ways that phishers trick people is through e-mails leading to fake websites often with the websites impersonating a legitimate domain like your banks website. One way they do this is by using a domain that looks similar to the legitimate domain.

Above would be an example of such an effort trying to mimic the google domain. Anything below this domain name can be tailored in an attempt to mimic the legitimate website.
Another way a phisher might attempt to conceal the fake website is through subdomains.

In this example a phisher is targeting someone’s banking details through SMS. The phisher references the bank in the subdomain name to look similar to the original websites URL. The actual domain name is uk-account.help; which is meant to mirror a legitimate website of hsbc.co.uk/account-help.
Even then sometimes you can still accidently access these websites often times the first thing you will see is a login page. This can often be a red flag if you are already logged into said service.
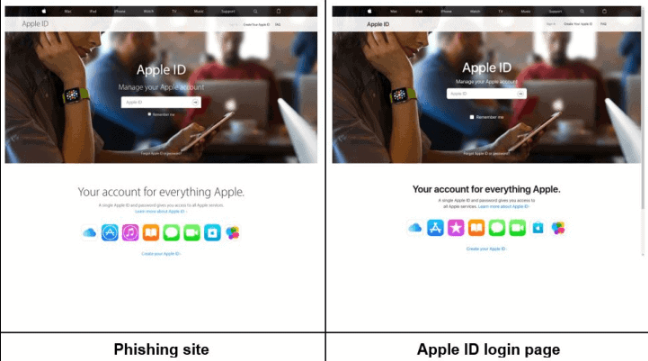
Even then you can notice slight errors from the legitimate website above. Phishing websites often just copy and paste information from the original and can be littered with small errors.
Week 7 – Journal Entry 7



All of the memes related to human-centered cybersecurity; more specifically towards social engineering. It highlights the importance of individuals being mindful of their online security practices and taking steps to protect themselves from phishing. It emphasizes how necessary it is for people to be educated about how easy it is to become susceptible to malicious actors on any platform be it mobile or computer systems. Malicious actors can use many a method to attempt to trick people into falling victim to social engineering as shown by the thoughts going on inside the minds of these individuals.
Week 8 – How media influences our understanding of cybersecurity
Media plays a role in how the general populace shapes their understanding of cybersecurity. In terms of movies it is often sensationalized with the “hacker” portrayed in some form of stereotype. Very few movies actually delve into hacking besides the surface level of using terms from the cybersecurity field and it will portray random strokes on a keyboard as hacking. Media also presents cybersecurity as a complex and difficult issue that the average person would not be able to easily understand. This might deter people from being proactive in implementing security measures on their personal devices. On the other hand news media raises awareness of cybersecurity issues such as large corporate breaches. By highlighting these examples of cyber attacks it can help individuals and organizations understand the importance of cybersecurity and the potential consequences if ignored. Overall outside of dedicated cybersecurity media most of the influence media has is a mix of positive and negatives for peoples understanding of cybersecurity.
Week 10 – Journal Entry 9 – the Social Media Disorder scale
https://www.brieftherapyconference.com/download/handouts/Tobi-Goldfus-Social-Media-Disorder-Scale.pdf
After completing the questions in the Social Media Disorder scale I scored 1 out of 9. My score reflects how little I’m involved with social media. When reflecting on the items listed on the scale it highlights how some might use social media as a coping mechanism, and how people who have addictive personalities might fall victim to becoming reliant on social media. It also highlights how people addicted to said social media will inevitably overshare and dox themselves on these platforms potentially to their detriment. As this information can be used for identity fraud or to stalk you. In terms of patterns found across the world it correlates to ones access to both technology and these platforms.
Week 11 – Journal Entry 10 – Social Cybersecurity
Social Cybersecurity is an emerging interdisciplinary form of cybersecurity. It focuses on the human element involved in computer technologies. With it exemplifies the need to protect against cyber warfare using social cyberwarfare. This is generally done by information and psychological means; think manipulating a narrative from a bot network spamming propaganda. Nations such as Russia are prime examples of a country utilizing this hybrid-warfare style due to their invasion of Ukraine. It shows how information in social networks needs some sort of cybersecurity protection to prevent external manipulation. Primarily like traditional cybersecurity the best method is through education, as informing people about the risks, the methods, and the reason why someone would want to manipulate information in their social spaces will help people understand when it is occurring.
Article Review #2: The Impact of Low Self-Control on Past and
Future Cyber Offending
Research Question/Hypothesis
The study proposes that with the proliferation of internet and personal technology
devices, that amount of people perpetrating cyber offending behaviors has also increased. The
researcher then seeks to apply the criminology theory of self-control to cyber offending as one of
the potential variables in this increase in cyber offending.
Research Methods
The researcher for this study obtained his data set from self-administered questionaries
filled out by under-graduate students during the spring semester in 2010. This demographic was
chosen due to students as individuals are more likely to engage in various forms of cyber
offending. Examples of this would be digital piracy; usually of media, and computer hacking. To
attempt to maintain a diverse set of data points the researcher sent the questionnaire to instructors
at the school that taught undergraduate students, in which it was spread out across various
majors.
Data and Analysis
The data size acquired for this study is 428 self-administered questionnaires. The sample
is then divided on the technicality of the major, their gender, and ethnicity. Some of the
important questions asked by the researcher pertain to the anticipation of future cyber offending,
such as password guessing, using a social network to retaliate against someone, accessing
computer files without permission, altering someone else computer information, and digital
piracy. This was then followed by questions designed to measure respondents’ self-control. This
data was then examined through the use of Ordinary Least Squares regression models, as well as
Logistic regression models.
Relation to Principles of Social Science
This study utilizes a key principle of the social sciences in the use of a questionnaire for
its research method. This can be considered social science research as it is attempting to
understand the underlying cause of a social issue of cyber offending. It is also interdisciplinary as
it draws on criminological theory.
Relation towards class curriculum
This study has significant overlap with Module 5’s power-point, in which it goes over the
psychological theories of cyber offending. Whilst it isn’t applying the theories learned in the
module it does seek to apply a psychological variable of self-control. It further has similarities
with Module 7 as it incorporates cyber bullying; in the form of using a social network to retaliate
against someone.
Relation to marginalized groups
Whilst the study does divide its data along ethnic and gender it does not relate to the
challenges, concerns, and contributions of marginalized groups. As the focus of the study is on
the individuals and their relation to cyber offending.
Contribution to Society
By being able to understand the underlying factors that contribute to cyber offending
behaviors allows for valuable insight into ways society can develop effective strategies to help
address cyber offending.
Conclusion
This study shows that traditional criminological theories can be used as a variable to
explain cyber offending. Its research method might have a sample bias as it does not have
samples outside of college students. Furthermore, the questionnaire whilst being a great tool for
social studies such as this might be biased towards people who successfully filled it out. Overall,
this study relates to both the social sciences and what we learned in class. As well as contributes
to the rise in research applying traditional theories towards cyber based crimes.
Reference
Nodeland, B., & Morris, R. G. (2020). The Impact of Low Self-control on Past and
Future Cyber Offending. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3742075
https://www.cybercrimejournal.com/pdf/NodelandMorrisVol14Issue1IJCC2020.pdf
Week 11 – Journal Entry 11 – Cybersecurity Analysts relation to social behaviors
The job description for a cybersecurity analyst highlights the importance of communication, collaboration, and teamwork. As utilizing effective communication skills as being able to explain something like a new phishing threat to someone who might not understand cybersecurity is crucial for success. Other social behaviors such as problem solving is necessary for an analyst. Similarly to a degree one needs to be able to work under pressure to address security threats. Overall as an analyst from entry level to more experienced positions social behavior such as communication is key to help people understand the holes in their security, new phishing attempts, or other emerging threats.
Week 12 – Journal Entry 12 – SAMPLE DATA BREACH NOTIFICATION and its relation to economic and social theories
Economic Theories
1. Cost-benefit analysis – By reporting to the customers about a breach the company is weighing the cost of responding to the breach (such as notifying affected individuals, investing in cybersecurity measures, and potential legal expenses), against the benefits of maintaining customer trust, avoiding fines/penalties, and protecting their reputation.
2. Supply and Demand – Furthering the train of thought by having a breach it is likely to have affected the companies reputation. As even informing your customers about a breach still gives a negative perception of it, this ultimately will lead to less demand and can impact prices.
Social Science Theory
1. Social Exchange Theory – The data breach notification letter may address the social exchange between the company and its customer. As it attempts to repair the trust in the company to keep data integrity.
2. Social Learning Theory – The company might have also suffered previous breaches which it handled in a less transparent way, leading to legal or social consequences. Therefor this is an implemented measure from learning from past mistakes.
Week 12 – Journal Entry 13 – Bug Bounties
As a policy bug bounty programs offered by companies act as a crowdsourced form of cybersecurity. It is something that will have efficacy no matter the size of the company or organization. Although the amount of valid reports will obviously vary, which may be influenced by the company; larger companies viewed as socially bankrupt might need to offer larger bounties and sift through more false reports. Furthermore, companies and organizations might need to update their bounties as vulnerabilities are fixed due to a smaller pool of people able to find said vulnerabilities. Overall as a policy it works as an effective tool to discover overlooked aspects by your own cybersecurity team.
Week 13 – Journal Entry 14 – Illegal Things You Unknowingly Do on the Internet

There are around 5 of these I would actually consider a serious violation. The first offense would definitely be collecting information about children, as minors deserve the highest expectation of privacy. The second offense that in my opinion can be a more serious violation is bullying, whilst bullying and trolling is fine between friends once it is turned towards random people on the internet or someone you perceive as deserving it quickly becomes malicious. The third violation I’d view as a serious violation would be using other people’s internet networks as even if people have incompetent security measures it does not justify accessing their network. The fourth would likely be illegal searches on the internet this one is probably on the lesser end of what I would consider a serious violation, unless it involves predation of children, as people can look up illegal things to satisfy macabre curiosities. The fifth would be recording VoIP without consent as like with most of these consent to record or use materials should be upheld.
Career Paper: Cybersecurity Analyst
Introduction
A cybersecurity career that requires and depends on both social science research and principles is a cybersecurity analyst. Cybersecurity analysts are tasked with protecting an organizations computer networks and systems from cyber threats and unauthorized access. Cybersecurity analysts due this by analyzing security data, monitor network, implement best practices, and develop policies to prevent and respond to cyber-attacks. Its dependence on the social sciences comes from the position of needing to understand both the behaviors of the threats attempting to breach as well as the employees which are often a target.
Social Science Principles
There is to a degree an application of the social science principle of determinism when it comes to the job of cybersecurity analyst. As from the perspective of the analyst there will always be a threat attempting to gain unauthorized access into whichever organization they are working for. So, in this deterministic expectation a cybersecurity analyst has to prepare policies to help mitigate this inevitable breach when a vulnerability is eventually found. This influences the day-to-day routines of a cybersecurity analyst as they scrutinize security data expecting to find potential irregularities which in turn would mean a potential breach.
Social Psychology principles are also relevant in the daily routine of a cybersecurity analyst. As one of the most common tactics used by threats is using social engineering to trick employees into either revealing sensitive information, or clicking on malicious content. This can occur from phishing, unsafe internet browsing, or using pretexting in which the offender impersonates someone important from the organization (Hadnagy, 2011). This shows the necessity that an analyst implements human centered cybersecurity policies to identify and educate employees about social engineering tactics, reducing the likelihood of successful attacks.
Social Science Research
Social science research is essential for cybersecurity analysts because it helps them understand the motivations and behaviors of cyber attackers. By studying social science research on cybercrime, cybersecurity analysts can better anticipate and prevent cyber-attacks. For example, if an analyst works for a healthcare organization, they might understand from their research that they are more likely to be targeted by threats looking for financial gain; as “the facts that they house sensitive information in their system, there is a higher probability of payment” (Kiser & Maniam, 2021). In which understanding this motivation means they should prepare for their organization to mitigate the impact of ransomware attacks.
Another avenue in which social science research is valuable would be in understanding human factors such as an employees’ perception and awareness of cybersecurity policies, and how they can influence their compliance with said security policies. For example, if the employee has not been trained or informed about a new cybersecurity policy such as a monthly password change, they are more likely to have a weaker password (Li, He, Xu, Ash, Anwar, Yuan, 2019).
Marginalized Groups
Marginalized groups, such as racial and ethnic minorities, LGBTQ+ individuals, are going to face unique challenges and vulnerabilities when it comes to cybersecurity. Cybersecurity analysts must consider them when helping to protect an organization from cyber threats. One of the ways is through inclusion within the analyst team itself ensuring there is a perspective that understand the more specific risks that might target marginalized members inside said organization. Analysts also have to consider the potential that the tools and systems that they implement might inadvertently perpetuate racial or gender biases, leading to disparate impacts on marginalized communities.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity analysts are dependent on both social science principles and research associated with the social sciences. Social science research plays a critical role in shaping the strategies and tactics used by cybersecurity analysts to safeguard sensitive information and ensure the security of organizational data. Whilst the social principles when applied help understand the mindset of expectations of a data breach as well as the psychological principles of social engineering. Overall, both are needed to effectively protect which ever organization has hired them to protect their computer networks from threats.
References
Hadnagy. (2011). Social Engineering [electronic resource] The Art of Human Hacking (1st edition.) (4.2 The Principles and Planning Stages of Pretexting).
Kiser, & Maniam, B. (2021). RANSOMWARE: HEALTHCARE INDUSTRY AT RISK. Journal of Business and Accounting, 14(1), 64–81.
Li, L., He, W., Xu, L., Ash, I., Anwar, M., & Yuan, X. (2019). Investigating the impact of cybersecurity policy awareness on employees’ cybersecurity behavior. International Journal of Information Management, 45, 13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2018.10.017
Week 15 – Journal Entry 15: Digital Forensics
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pf-JnQfAEew
This speaker of this Ted talk goes over his opportunities that led him down the path of digital forensics. It shows how following your interests in your career can help you find a niche that can blossom into other potential changes in career. It is similar in some cases with my own experiences as I found I am more talented on finding out how to break things doing QA work which led me to want to become educated more in cybersecurity. Overall nothing is set in stone when it comes to finding work that you enjoy continuing to explore interests and educate yourself in my opinion is key to help finding stuff that you can be passionate working on.
